Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases
In 1990, Dr. Rath and Nobel laureate Linus Pauling published research showing that chronic vitamin C deficiency causes damage to the epithelium of the veins. As a natural response, the body deposits lipoproteins Lp (a) on the vessel walls to repair them. Over time, this results in the formation of plaque on the vessel walls, causing the vessels to clog.
The human body, unlike most animals, is unable to produce vitamin C itself. Therefore, to protect ourselves from cardiovascular disease, it is very important to get enough vitamin C. Vitamin C thus plays a crucial role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease.
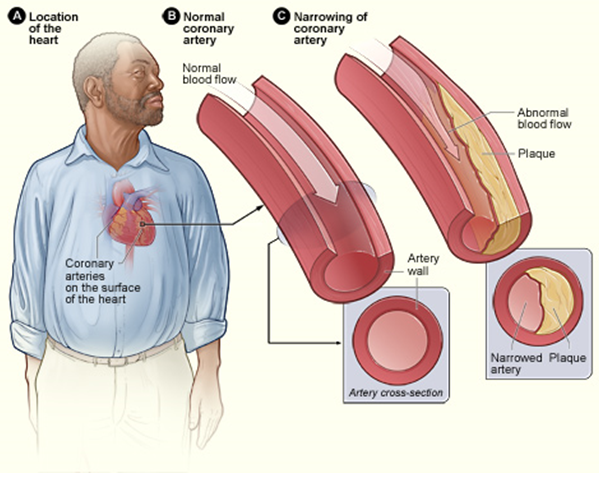
What is Arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is the name for the deposition of fatty substances on the wall of arteries. This causes the vein wall to thicken and become less elastic. An artery consists of three layers:
- an elastic outer layer composed of connective tissue
- a muscular interlayer
- a thin inner layer
Arteriosclerosis involves the thin inner layer of the arteries. The aorta and coronary arteries are the veins in which arteriosclerosis is most common.
The importance of vitamin C:
Most animals cannot have a heart attack. For humans, this is different. We will elaborate on that connection here.
As humans, we cannot produce vitamin C. In prehistoric times this was still the case. The founder of orthomolecular science Linus Pauling has the following explanation for this:
Tens of thousands of years ago, humans lived in an environment where plenty of vitamin C was available in the form of plants and fruits. As a result, it was no longer necessary for the human body to make its own vitamin C. In other words, a genetic change has taken place that prevents us from making our own vitamin C.
A long-term vitamin C deficiency can lead to the well-known disease scurvy. Today our diet provides enough vitamin C to prevent scurvy, but unfortunately this amount is insufficient to maintain healthy vessel walls. Vitamin C deficiency causes small tears in the vessel wall.How do we prevent this damage to the vessel walls?
Getting enough vitamin C can prevent damage to the vessel walls. With the findings of Dr. Rath and Linus Pauling, we can say that there needs to be a reorientation in the approach from 'too high cholesterol in the blood' to 'too low presence of vitamin C'. This will allow us to look at cardiovascular disease preventively and from a therapeutic approach.
To measure is to know:
Measurement of blood vessel quality is now possible through two independent readings:
- Loss of function (Augmentation Index ix) of blood vessel permeability: this is a measure of the joint resistance of the smallest blood vessels. The heart must pump against this resistance with every beat. Increased resistance results from incipient damage to the inner lining or cramping of the blood vessel wall. In either case, the heart must work extra hard.
- Stiffening of blood vessels (Pulse Wave Velocity - PWV) or vessel wall damage/calcification of the large body artery, the aorta. The higher the PWV value, the stiffer the aorta has become due to arteriosclerosis.
This measurement is non-invasive and is similar to a blood pressure measurement.
Vein Recovery Plan:
- Vitamin C
- Lysine
- Nutrition (reduce pro-inflammatory foods)
- Vitamin K2
- Exorphin free food
Our doctor may also suggest an IV protocol (lipoplaque).

Treatment BeterKlinic
BeterKliniek is the clinic for Integrative Medicine that bridges regular and non-regular medicine.
An van Veen (physician) and Michael van Gils (therapist) look for the cause of a condition or disease. That is where the treatment starts otherwise, as people often say, it is 'carrying water to the sea'. We call this cause medicine. Sometimes it is also desirable to treat the symptoms (at the same time). We call this symptom medicine.
Chronic disorders often have their cause in epi- genetics. You can schedule a free informative telephone consultation (phone number 040-7117337 until 1 p.m.) at BeterKliniek to discuss your symptoms so that we can provide you with further advice.

